Driver-assisted features continue to become more common in today’s vehicles. In recent years, technology like Active Cruise Control (ACC) or Lane Departure Warning Systems (LDWS) were more of a novelty — something consumers didn’t quite understand or feel the need to pay for. However, many newer cars are now equipped with these features as well as new ones like Lane Keep Assist (LKA) or even Park Assist (PA). In fact, US vehicle manufacturers are beginning to commit to technology that follows advances in Europe, where New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) standards require quicker adoption. For example, many US manufacturers are committing to every car having Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) by 2020. Cost and reliability of new sensing technology is helping to drive advancements in driver-assisted features, thus increasing the demand and affordability for customers.
While many early advancements relied on radar, more advanced sensing technology is being developed to further detect surroundings. Lidar can operate as a new tool for high precision detection, in real time, with object identification. The development of this technology brings us one step closer to fully autonomous vehicles.
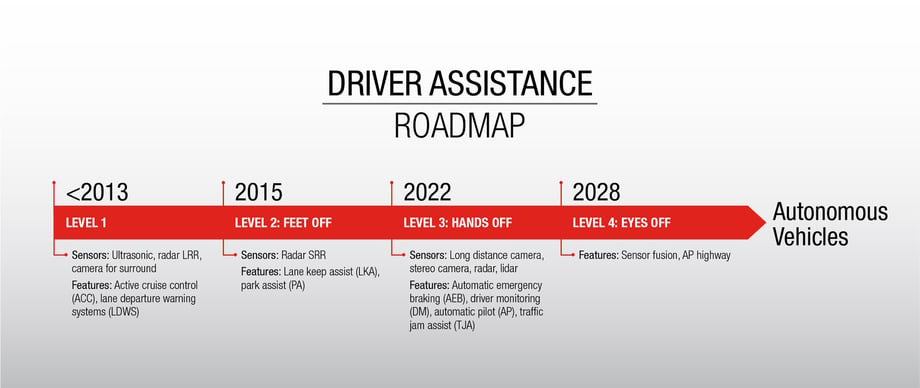
[See the full driver-assisted technology roadmap below.]
Here, we explore both short and long term trends that we can expect to see.
1. Changes in Our Preferred Way of TravelingIt’s possible we will see a shift in the transportation of choice when autonomous cars are fully operational and accepted. Right now, the majority of frequent travelers will choose to fly longer distances if given the choice between flying and driving. Even when factoring in the higher cost and longer time associated with security lines, traveling to and from the airport, and possibly renting a car at a destination, a 2-hour flight has historically proven to be more appealing than a 10-hour car drive. A large reason for this is the attention to the road that's required, preventing the driver from working or answering emails. However, autonomous vehicles will offer the ability to travel while sleeping or working. In comparison to current transportation methods, this is most similar to taking a bus or train with the benefit of having your own space, schedule, and generally, a faster trip.
In a recent poll summarized by Physics.org, the ability to take a self-driving car resulted in decreased interest in taking a plane in about 10 percent of people that fly. The interest in taking a drive vs. a plane was most significant in driving trips in the 7 to 11-hour range, especially if an individual would require a vehicle upon arriving at their destination. However, the study examined trips as long as 45 hours and found that 1 in 6 people would take the autonomous car ride over a plane ride even at that distance.
2. Increased Efficiencies in Productivity & CostA recent report suggested that almost 7 billion hours, and over 3 billion gallons of fuel, are lost to driving in traffic every year. One major area autonomous vehicles could impact is the ability to avoid crowded routes and limit the number of accidents that typically cause bottlenecks. Tied to many of the same safety related impacts, traffic speeds could also increase if widespread adoption takes place.
In addition to limiting travel time, those who generally drive will now become passengers. In terms of cost of productive time, a passenger still incurs expense, but less so than a driver. As mentioned above, with the introduction of level 4 technology, individuals will be able to more readily answer email, complete work, or even catch up on sleep while moving to their next destination. Non-work-related productivity will also be impacted. It is estimated that the time cost of driving for errands will drop by 30 percent.
A study (America’s Workforce and the Self-Driving Future) prepared for “Securing America’s Future Energy” estimates the gain associated with cost of productivity is close to $220 billion. The average savings could range based on the individual due to salary, commute times, location, and additional dependents. However, individual recouped time is expected to be noticeable. In some economic simulations, an individual could re-coup as much as $4,000 - $5,000 a year in gas, vehicle, and time savings.
3. SafetyIt should come as no surprise to hear that over 94 percent of vehicle accidents are related to driver error, many related directly to distracted or reckless driving. According to the 2018 Global Status on Road Safety from the World Health Organization, automobile accidents are the leading cause of death of people between the ages of 5 to 29 years old. Safety is perhaps one of the largest advantages of autonomous vehicles and the primary factor of other major impacts. For the identified age group above, it is believed that advanced driver-assistance systems, or ADAS, technologies could prevent 62 percent of accidents. By eliminating the human’s need to make decisions, react to changes on the road, or even pay attention, roads will become safer. Drivers will operate as predictable systems and more often comply with safety standards such as speed limits, distance between cars, etc.
To put this advancement into perspective, crash and driving data estimates societal costs are currently over $1 trillion a year; it could be expected to see an annual benefit of $500 billion from limiting just human error-related accidents.
4. Increased Job Opportunities for Individuals & Hiring Market for CompaniesAutonomous vehicles have the potential to impact job opportunities as well. For example, opportunities for employment increase for those who face barriers due to lack of transportation or the inability to take public transport for health or disability reasons. The entire population will also be more motivated to travel farther for work due to less stress, cost, and time associated with a long commute.
An increased interest in travel will directly benefit companies, allowing hiring managers to choose from a larger labor market to find the right expertise for open positions. In some scenarios, this market size is estimated to increase by 15-18 percent. The following graphic demonstrates calculations for several areas:
Job Increase Due to AV-Enabled Commutes
|
City |
Current Jobs in Commuting Distance of City Center |
Jobs in Commuting Distance with AV-Enabled Commute |
Percent Increase |
|
Niles-Benton Harbor, MI |
63,035 |
206,945 |
228% |
|
Gary, IN |
388,802 |
1,225,216 |
215% |
|
Elmira, NY |
58,636 |
123,805 |
111% |
|
Wilmington, DE |
492,500 |
1,479,969 |
201% |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
5. Ridesharing Efficiency & Energy Security
One of the first areas of implementation for autonomous vehicles is rideshares. As the technology will take some time to become affordable for the individual, this market offers a significant opportunity for taxi companies or other services such as Uber to offer “robo-taxis", or automated shuttle services. Additionally, this technology is currently evolving alongside hybrid and electrical vehicles creating potential synergies for both rider and environmental efficiency.
58 percent of current autonomous vehicles are based on an electric platform, while 21 percent are on a hybrid platform. Increased access to this type of technology allows increased diversification of energy sources. As the impact on gas consumption from decreased congestion is expected to be the equivalent of 80,000 barrels of oil a day, this decrease in reliance will surely also impact the energy sector.
While there are many debates in the market on building the ideal situation, the earlier mentioned impacts can be expected as we reach widespread adoption of level 4 autonomous vehicle technology. To learn more about lidar’s place in this type of system, check out some of our related resources.
- Environmental Conditions that Impact Laser Diode Design for Automotive Lidar
- Making Waves: Nanosecond Pulsed Drivers for Flash Lidar
If your team has questions regarding the development of your sensing system for automotive applications, contact us today.